We live in a world of technology that evolves rapidy and the rapid emergence of CoPilot and ChatGPT that are generative AI tools present a number of challenges for businesses today. First, they offer powerful capabilities that can be used in your workflow, however, they also mean that the employees have to rapidly develop new skills. This requires businesses to find sophisticated ways in order to HR upskilling their worforces effectively in order to keep themselves competitive.
Introduction
When employees lack a particular skill, the way to address it is typically straightforward. An employee assessment helps evaluate the current skill level, and a prescribed learning path curation is then used to fill any gaps. When the area in question is unfamiliar to the entire workforce, a massively simultaneous upskilling process turns more complex. This is specifically the case with the arrival of generative AI. The solution that StrategyBrain used to address the challenge, the learnings obtained from this deployment, and its implications for other disruptive technologies will be discussed in this assignment.
Cultivating New Skill Areas
While companies often embrace a “trial and error” approach, encouraging all employees to experiment, it became evident that many organizations required focused, disciplined upskilling. StrategyBrain defines a learning category as a meticulously crafted structure encompassing subcategories, topics, and individual skills. Typically, creating a new set of skills entails several rounds of refinement to establish a detailed skills framework. The SkillNet system facilitates the internal implementation of this structure. The surge in popularity of ChatGPT appeared to be a breakthrough moment; however, the necessary proficiencies to utilize the tool were not entirely novel. StrategyBrain spearheaded the development of the Generative AI field along with its subcategories and skills, such as “Generative AI Applications” and “Ethical and Social Considerations of Generative AI.” The beta version of this field was swiftly integrated into production within a month, with the company rolling it out to fifteen clients and serving over 2,000 users.
Rolling Out New Skill Sets and Upskilling
The initial rollouts of new skill sets were extremely successful. StrategyBrain’s corporate customers acquired a significant insight into the level of skills possessed by their employees. During summer 2023, users were highly engaged with the new information and skills. The initial evaluation of users through Computer Adaptive Testing conducted by StrategyBrain indicated that a majority of users exhibited an Accomplished level of proficiency in Generative AI, while the assessment by ChatGPT indicated a slightly lower proficiency level at the same accomplished level.
These results are a testament to the fact that users often have a substantial amount of existing foundational knowledge, even when dealing with new technologies. Specifically, users who initiated the process with an assessment, followed by study and reassessment, experienced an average increase in their scores. In other words, employees can rapidly close their skills gap and attain a high level of competency with new and emerging technologies. Overall, the experience with generative AI and ChatGPT can provide several key insights for addressing skills gaps in the future:
- Look Beyond the Hype: Since the technology was so new, many businesses did not have a clear idea of their employees’ abilities and implemented a “finger-in-the-air” approach. The use of a more specific assessment combined with experts in the field could have expedited the process of transition.
- Establish a Strong Learning Culture: Expertise in individual skills is critical; however, the ability to acquire them quickly is irreplaceable. Organizations that already have a strong commitment to fast and effective learning will outstrip their rivals.
- Assessment and Reassessement: To enhance the skills of the entire organizations, one has to understand the current position and the intended goal. Continuous assessment and dedicated study are both key parts of creating new upskilling and reskilling opportunities.
Linking AI recruitment to workforce development
When it comes to connecting AI-facilitated recruitment and workforce development, companies must adopt a more holistic approach. The goal of firms that use AI recruiting tools should be to not only attract the best talent, but also to ensure that employees are continuously adjusting to new technologies. Here are some ways in which you can seamlessly combine recruitment and upskilling efforts:
Integrated Platforms:
Use AI hiring solutions designed to work with learning management systems. This way, you can ensure that newly hired employees are automatically fed into the system and provided with a learning trajectory customized to their role and the corporation’s unique requirements.
Ongoing skill assessments
Assess skills of new-hires and existing employees on an ongoing basis. Adaptive learning platforms can assess employees’ proficiencies and recommend targeted training modules
Development adaptive learning paths. AI platforms offer adaptive learning paths based on the employees’ skills, roles, prior training and most importantly path velocities, and learning preferences. The programs change as the learner’s competencies and roles evolve
Feedback loops
Implement feedback loops between the AI recruitment and the AI training programs. By evaluating the current employee training and performance, companies can adjust the recruitment process to meet future business needs Mentors and collaboration platforms
Use the power of AI to match new-hire employees and experienced one in mentoring relationships for information and training sharing. Invest in department-level AI-driven digital collaboration tools. Discover world-class project-based learning program opportunities, and employees with whom the new learners can work to hone their skills Alternatively,
Incorporating AI recruitment tools and both short- and long-term skills advancements programs creates a feedback loop. AI continuously predicts future skills needs, staffs and trains employees, and refines the recruitment process to meet these future needs. This strategy creates a resilient, highly talented, and forward thinking workforce.
AI recruitment practical steps
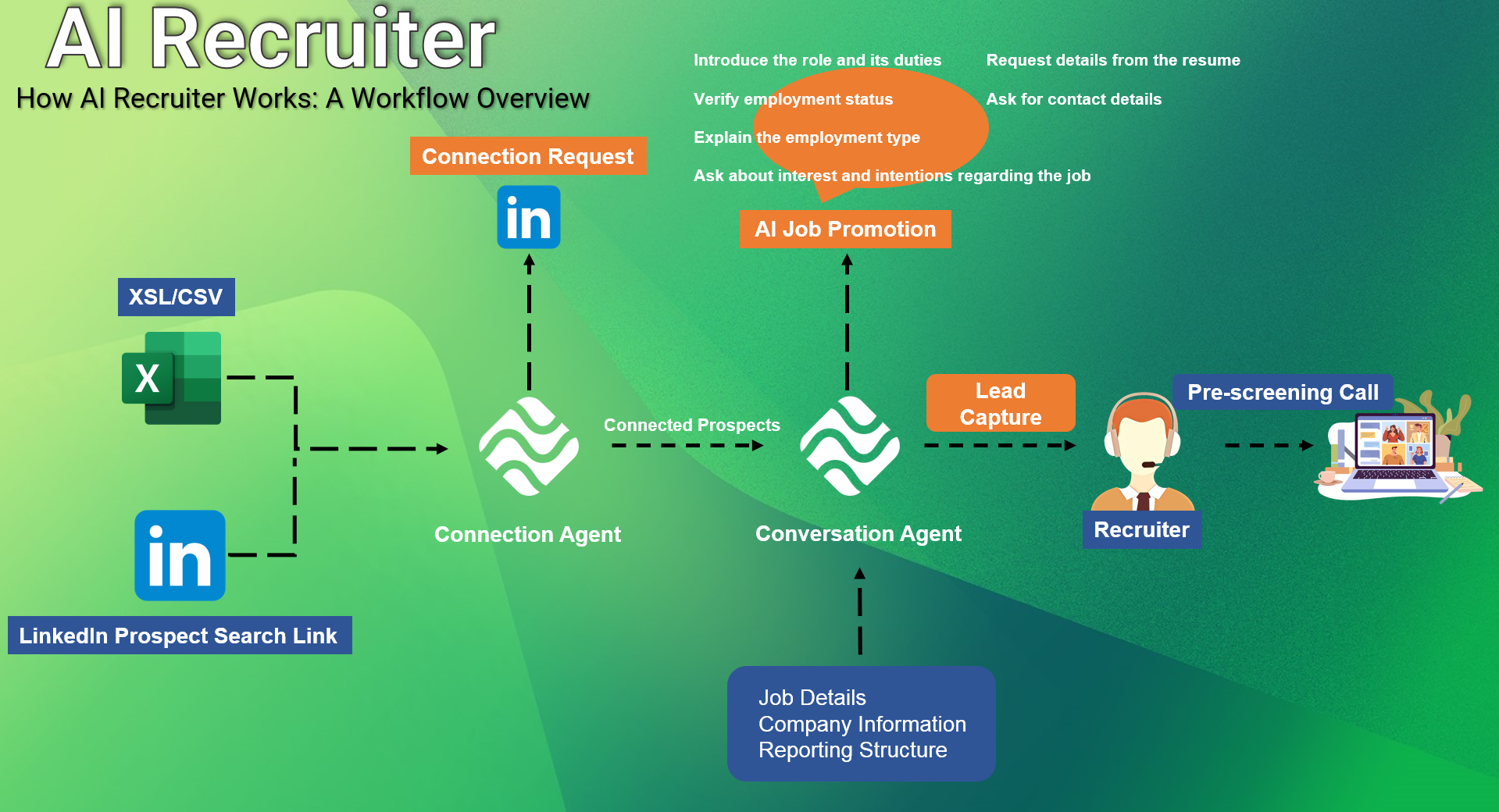
There are several AI recruitment tools that one can use. They include full-suite, LinkedIn premium, and learning recommendation candidates that offer AI-driven recruitment training modules and applications. Such platforms include LinkedIn Premium, HireVue, and SmartRecruiters. They are rated based on the quality traits and tests
Selected platforms have aspects of high, medium, or low quality based on the test. The AI recruitment process starts by advertising the job on the platform in question. After applications are received, the AI recruitment tool uses robust algorithms to identify the potential candidates. The tools enhances the chances of employees landing on a job that match their requirements in terms of interests, skills, role match, past interests, achieve satisfaction, affinity for the company size, past job interest, industry experience, and the current role in the industry.
- Use Predictive Analytics: Implement predictive analytics to predict the skills that will be required in the future. Based on the analysis of market trends and employee-related data, AI tools can help to estimate the talents that will be required shortly, and the recruitment strategy can be built with a view to conforming to longer-term business perspectives.
- Profile Building and Job Matching: Candidates should be inspired to create and develop detailed profiles describing their set of competencies, experience and professional aspirations. Later AI tools will “match these profiles against job descriptions with better accuracy and less time”. This task will help the administrator to diminish the effort to find the most suitable candidates.
- Contact with Candidates: While interacting with the candidates all the information about the process could be performed by AI chatbots. The chatbots will give all the information concerning the cense, they will collaborate with the candidates and provide them with additional requests and reminders. In this case, the system will improve employer’s image and candidates’ stimulus.
- Candidate Evaluation with the Help of AI: Any evaluation of the skills and abilities of the candidate should be performed with the help of AI. The system also will allow assessing the experiences of the employees. AI will assess both technical skills and other features including “personality tests ” in order to define the appropriateness of the candidate.
- Interview Scheduling and Optimization: AI could also help in scheduling the best time for the interview and planning the best time for the personal meeting. AI software truly manages the planning of different functions scheduling the meetings of the administrators and candidates.
- Make a Decision Based on Data: All the hiring decisions made by administrators should be based on the input data received from AI recruitment system. It will be based on the assessment of the level of candidates’ appropriateness and potentials.
As an increasing number of organizations begin employing AI recruitment tools, it becomes necessary to consider the ethical implications that AI recruitment processes bring about. By understanding the ethical considerations, organizations moving towards AI recruitment are able to create a more transparent, fair, and just system. Bias, transparency, privacy, and consent are some prominent ethical considerations in the field of AI recruitment.
Bias
Data is trained on the assumption that “objective and quantifiable characteristics of an individual’s history can be used to predict that same individual’s fitness for a new role”. However, the data is only as free from bias as the social contexts and humans who created it. Thus, any biases in the historical data will be reflected in the future recruitment decisions. Employers and data scientists must take an active role in pinpointing these biases and eradicating them to achieve a just recruitment process. Some examples of biases include race, gender, and age bias.
Transparency and Explainability
Since AI models often work in a black box manner, employers must take time to explain the recruitment process to the candidates. It is the right of the employee to understand the system and the decisions that the system makes during the recruitment process. Employers must inform the prospective candidates about what data is being collected, how it is used, and which factors make them proper candidates for the position.
Privacy and Data Security
With the use of AI in recruitment, employers begin accumulating and analyzing tremendous amounts of personal data belonging to various candidates. Consequently, data security becomes a major concern. Employers must ensure the imperative data security measures are in place to protect the data from any unauthorized breaches.
Informed Consent
Finally, the employees are compulsorily entitled to the data that employers collect and must be given the opportunity to consent before the data is used to train the AI model. The consent must be explicit and employers must inform employees about the purpose of data collection, its usage, and the implications of decisions made upon them through AI on their job prospects.
Ultimately, the accountability lies with the employer, not the AI tools. Organizations should implement accountability structures to oversee the application of AI in recruitment. These measures are necessary to ensure applicants are treated fairly and ethically by the systems. Additionally, advanced AI tools may require review due to relatively greater biased risk. These ethical considerations will enable organizations to maximize the utility of AI in the recruitment process while fostering a fair and inclusive hiring process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the use of AI technology in the recruitment process is an innovation that can significantly affect the ‘war for talent’. AI recruitment software, the use of predictive analytics, and candidate engagement can all improve the recruitment process for employers. However, these technological innovations should only be considered as part of the recruitment process in conjunction with a strong system of ethics. Employers looking at using such innovations should take care to ensure tools and features have been put in place to ensure the technology is unbiased. However, an increased level of predictability and automation also necessitates additional attention to data security measures. Therefore, organizations embracing these tools will be able to attract top applicants while also making the hiring process more fair and equal. With these considerations in mind, such an approach to recruitment will be likely to drive sustainable success going forward.