Introduction
One notable change brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic was the shift towards remote work, becoming the norm rather than the exception. In 2021, 32% of Canadians aged 15-69 worked from home, a significant increase from just 4% in 2016. This change reflects a broader trend in the transformation of work environments and practices that extends beyond the pandemic itself. In the U.S., over half of the working population now has the option to work remotely, leading to a reconsideration of nonresidential workspaces and an increase in demand for in-house working equipment. Before the pandemic, 43% of the workforce occasionally worked from home, indicating that these trends were already in motion. This highlights the crucial role of AI recruitment technologies and digital communication tools in rethinking work practices to integrate more flexible arrangements, mirroring trends observed prior to the outbreak. While the actual and potential implications of these developments remain to be fully assessed, it is clear that the future of work will be markedly different from the past.
New Normal in Remote Work Productivity
The New Normal
A survey in the Slack workspace of more than 9,000 knowledge workers revealed that 72% of them preferred hybrid work models. The preference for remote work was expressed by 12% of respondents, while the remaining 16% were willing to return to the full time in office. Benefits of remote work without a doubt exist, and they hardly need to be proved. A key advantage is, of course, saving time and money that would have spent on »commuting« to the office. Allowing workers to manage their private live better, the employees will be able to be much more productive and satisfied with their job. Similarly, the low efficiency of work should not be considered as wasting time during the main workday. At the same time, a collective one, for in-office work has no alternatives — team building, the spontaneity of personal communication, and the development of a collective subconscious environment are undoubtedly the advantage of this work. Especially when it comes to maintaining a specific corporate culture or business, which is difficult to convey otherwise. Moreover, such work also provides the rigidity of this framework, which for a certain number of employees is noteworthy. The balance of these modalities can be an entirely workable and very prosperous approach in which technology is used to facilitate office work rather than completely replace it. Moreover, even aside from the exact work model, the transition to a remote mode leads to a significant increase in labor efficiency.
Productivity in remote work and financial benefits of its introduction
It is important that due to such an approach, remote work does not just increase labor productivity but is also very useful for employees and employers in a financial sense. It has been noted that employees operate more effectively at home, and a significant reason is the reduction of stress levels due to uninformative conversations and office stresses. This leads to a tenfold reduction in error levels. In addition, work remotely for those specialists whose results are more prioritized than »counting how many hours your existing employees are in». The company also stops seeing most of the costs or cut them, in particular, renting large offices.
As companies look to cut costs associated with renting and maintaining office spaces, both companies and employees can save money by working remotely. A company can direct some of the funds that go to rent out offices, utility bills, and provision of onsite services, such as a gym for employees, to the development of its employees and running of other innovative projects. Equally, an employee can save on travel expenses, as well as daily expenditures, such as lunch, work clothes, and those associated with traveling from their residence to their place of work. In many ways, as companies become well adjusted to the new normal, it is becoming highly evident that the remote working arrangement not only helps to increase productivity but also saves costs associated with some of the operations mentioned in the preceding text.
Remote Onboarding and AI
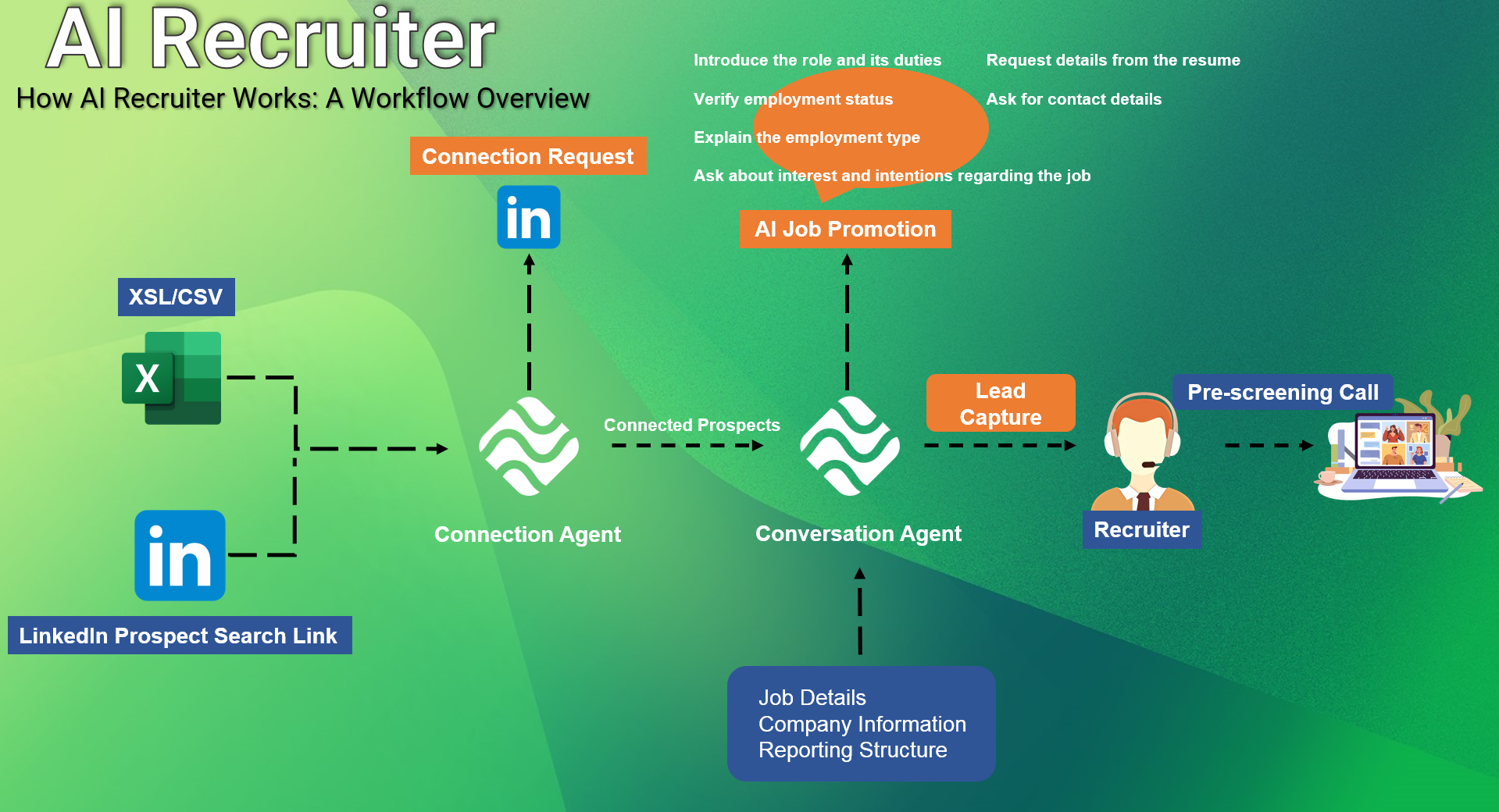
Both COVID-19 and remote working have redefined the meaning of hiring onboarding processes. AI, including tools such as videoconferencing software, and AI-based applications that can be used to analyze job applications, screen potential employees, and engage with applicants, have become particularly invaluable to hiring managers as they adjust to the new normal. A company can fill any position in its ranks from any part of the world or wherever else the best talent might be located. Moreover, the reliance on remote onboarding using such technologies and processes to engage new hires comes at a time when up to 20% of new jobs were already being posted online in the period leading up to the COVID-19 outbreak. In other words, COVID-19-related disruptions have not only accelerated the growth of other less manual approaches to the process of onboarding but also recruiting. At the same time, AI recruitment tools stand out as especially invaluable as they can be used to screen distributed applications more efficiently and possibly identify the right employees within a given talent pool for a particular job without going through the tedious process of hiring managers perusing through the thousands of job applications. Equally, the use of AI to recruit employees can attain a sufficient level of accuracy in the hiring process and expose businesses to a low risk of being accused of bias.
It follows from the above that the use of AI in the recruitment process provides numerous benefits to both employers and employees. On the one hand, it enables businesses to identify the most promising hiring patterns, candidates, and sources by processing vast amounts of data. In particular, this technique is effective in identifying the degree of fit based on previous job match and tenure, thus having a profound effect along all stages of the hiring and onboarding process. Additionally, AI software makes it easier to adjust criteria to find a validated fit while considering the ever-changing demands of the job market. This allows HR teams to hasten the finding and hiring of the most promising candidates and reduce the workload of ensuring a smooth onboarding process. With all the advantages in mind, one might conclude that the use of AI technology allows businesses to build more adaptive teams that are better integrated.
The New Normal of Hybrid Work and Its Relationship with AI Recruitment
As the hybrid work model is gaining ground, its relationship with AI recruitment is more crucial for employers looking to hire and keep the best candidates. With the help of an AI solution, hiring managers can perform their tasks much faster given that they typically need to hire from both remote and in-office pools. AI tools can sift through the submitted resumes and other information, find the best candidates according to the criteria set by the employer, and avoid making bad decisions with the help of expert dataset knowledge. What is more, in a hybrid work scenario, it is crucial for employees to properly act in the team, which requires a good fit to the company culture. AI tools can analyze this aspect along with other data to ensure employees are suited for hybrid work in the remote and live sections of the office. In other words, in the new normal, there is no going back, and the necessity of using AI for recruitment and other related purposes is not a choice but rather a precondition for building a multisensory and diverse staff that can perform well in the new normal setting.
The Role of AI Hiring Tools in a Virtual-First Work Environment
AI hiring tools make a significant contribution to a virtual-first work environment because they ensure efficient remote recruitment and help keep the team together. These tools help streamline the hiring process, and organizations can leverage such AI to identify and attract the best talent worldwide. Using AI for hiring purposes, companies can become more competitive. In addition, these tools enable automation of many routine processes, such as candidate screening and interview scheduling. As a result, HR professionals can save a lot of time and use it to build relationships with candidates and turn them into employees, contingent workers, or other categories of recruits.
Thanks to the use of these technologies, organizations can conduct not only the hiring activities but also team-building exercises and ensure that the team working remotely stays together. Oftentimes, such tools use advanced analytics that can provide information regarding the frequency and quality of team interactions. As a result, organizations can see where support is needed and can initiate virtual team-building sessions. In addition, HR professionals can communicate the results of such surveys and the action plan to their teams to make sure that the employees feel involved and supported. The AI hiring tools can help ensure that the recruitment process in a virtual-first work environment is accompanied by other activities aimed at creating a solid and cohesive team and improving HR processes that are possible with people working in the office.
Best Practices for Integrating AI into Recruitment
Overall, organizations should implement several best practices when integrating AI into their hiring processes. Most importantly, HR professionals should clearly define the objectives they want to achieve deploying AI tools. These objectives can include reducing time-to-hire or enhancing candidate quality. In addition, these goals should be specific. For instance, organizations should define how much they want to reduce their time-to-hire and by when.
Secondly, one should invest in the training of the hiring teams uttermost. Properly taught how to use the technology, employers extract more value out of AI tools, fostering their advantages and using them to significance. Provided with a deeper understanding of the tools’ functions and potential faults, employees can be more responsible with their use and will be less skeptical or afraid of making mistakes. The training should be ongoing to adjust to developing technology and constantly improve the quality of screening. Relating to the humans’ abilities, AI should not replace but enhance and contribute; automatic processing of resumes and scheduling of interviews should eliminate some of the most time-consuming routine tasks. Further, candidates enjoy and appreciate attending empathized interview with the human recruiter. The personal attention from potential employees would also make a positive impact on the organization’s employer branding. Lastly, employers should monitor the effectiveness of the tools. Specifically, such factors as candidate satisfaction from the process, the diversity of workforces, and percentage of the right hires should be observed. Flexible and agile in adapting to novelties, employers should shift their strategies each time their goals change. Taking all this into account, the technology helps deal with the current and prospective demands via effective tools, and convert the risks into advantages.
Case Studies
Case 1:A Global Tech Company
A global leader international tech organization avails of automated AI screening of resumes and pre-scheduling of the interviews worldwide from the very start each employee is offered to benefit from. The organization reports a 30% shorter time-to-hire as the procedure is carried out without interruption and in half the time. Accordingly, HR managers are capable of hiring more people with a higher employee success rate, demonstrating a 25% lower role leaving rate in the next two years. Most importantly, the brew software application is cast for the adequacy of the software competence, education, and organizational match of the teams, and helps avoid unconscious gender biases. As a result, with the hiring managers engaging with the broader and more fruitful mash, the previous avails thereof preserved through the accumulative cultural preferences remained in the ratey competitive pack of tech leaders.
Case 2: A leading healthcare provider
The provider implemented AI recruitment technologies to address biases related to different aspects and hire a more diverse team. In particular, the organization used an algorithm designed to ensure equitable selection criteria. As a result, the number of applications from underrepresented groups increased by 40%. The use of AI automated the screening process and enabled a blind overview of submitted resumes, thus, eradicating unintentional biases. The healthcare provider built a more diverse and inclusive team, which had a strong impact on the improvement of workplace morale and patient care. In this way, another successful application of AI recruitment technologies is related to their effect on the organizations’ inclusivity.
Case 3: A retail giant
The company implemented AI recruitment technologies based on its decision to create a hybrid work environment. In this case, the company needed to align its hiring practices with the new operational structure and focus on new criteria of employee compatibility. As a result, the initial onboarding failures were reduced by 35%. The AI platform focused on the evaluation of ultimate employee potential and compatibility between candidates and the hybrid work if the hiring managers made their decision considering these criteria. The company’s ability to hire employees suitable both for working from home and in a store had a positive effect on the employee satisfaction index, which increased after the new model was implemented. Two examples presented in this paper prove that AI recruitment technologies can significantly affect hiring and successful incorporation of employees in the companies, as well as they address the organizations’ strategic goals related to current social trends and operational practices.
Conclusion
The role of AI in the recruitment process is not a mere trend but a fundamental change which facilitates the efficiency and sophistication of hiring practices in the new competitive environment. Organizations can deploy AI tools to optimize routine activities and create an inclusive and diverse workforce capable of rapid adaptation to new challenges. Moreover, several case studies demonstrate that AI not only improves recruitment but also helps firms develop more effective and cohesive teams. However, employing AI efficiently and responsibly require adherence to the best practices, including defining objectives for the tools, training of the workforce, incentives, guaranteeing a human touch, and consistent tool adjustment. In such a way, businesses can benefit from the capacities of the AI technologies while adapting to the new opportunities and threats presented by a rapidly changing environment.